4.4 弹性布局(Flex)
弹性布局允许子组件按照一定比例来分配父容器空间。弹性布局的概念在其他UI系统中也都存在,如 H5 中的弹性盒子布局,Android中 的FlexboxLayout等。Flutter 中的弹性布局主要通过Flex和Expanded来配合实现。
4.4.1 Flex
Flex组件可以沿着水平或垂直方向排列子组件,如果你知道主轴方向,使用Row或Column会方便一些,因为Row和Column都继承自Flex,参数基本相同,所以能使用Flex的地方基本上都可以使用Row或Column。Flex本身功能是很强大的,它也可以和Expanded组件配合实现弹性布局。接下来我们只讨论Flex和弹性布局相关的属性(其他属性已经在介绍Row和Column时介绍过了)。
Flex({...required this.direction, //弹性布局的方向, Row默认为水平方向,Column默认为垂直方向List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],})
Flex继承自MultiChildRenderObjectWidget,对应的RenderObject为RenderFlex,RenderFlex中实现了其布局算法。
4.4.2 Expanded
Expanded 只能作为 Flex 的孩子(否则会报错),它可以按比例“扩伸”Flex子组件所占用的空间。因为 Row和Column 都继承自 Flex,所以 Expanded 也可以作为它们的孩子。
const Expanded({int flex = 1,required Widget child,})
flex参数为弹性系数,如果为 0 或null,则child是没有弹性的,即不会被扩伸占用的空间。如果大于0,所有的Expanded按照其 flex 的比例来分割主轴的全部空闲空间。下面我们看一个例子:
class FlexLayoutTestRoute extends StatelessWidget {@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return Column(children: <Widget>[//Flex的两个子widget按1:2来占据水平空间Flex(direction: Axis.horizontal,children: <Widget>[Expanded(flex: 1,child: Container(height: 30.0,color: Colors.red,),),Expanded(flex: 2,child: Container(height: 30.0,color: Colors.green,),),],),Padding(padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0),child: SizedBox(height: 100.0,//Flex的三个子widget,在垂直方向按2:1:1来占用100像素的空间child: Flex(direction: Axis.vertical,children: <Widget>[Expanded(flex: 2,child: Container(height: 30.0,color: Colors.red,),),Spacer(flex: 1,),Expanded(flex: 1,child: Container(height: 30.0,color: Colors.green,),),],),),),],);}}
运行效果如图4-13所示:
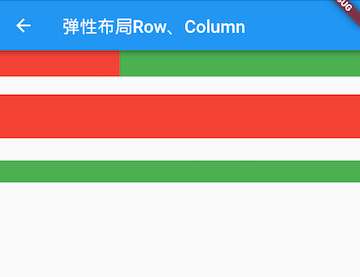
示例中的Spacer的功能是占用指定比例的空间,实际上它只是Expanded的一个包装类,Spacer的源码如下:
class Spacer extends StatelessWidget {const Spacer({Key? key, this.flex = 1}): assert(flex != null),assert(flex > 0),super(key: key);final int flex;@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return Expanded(flex: flex,child: const SizedBox.shrink(),);}}
4.4.3 小结
弹性布局比较简单,唯一需要注意的就是Row、Column以及Flex的关系。